Fiber Laser Cutter
A fiber laser cutting machine is an automatic cutting tool that uses glass fiber with rare earth elements as the gain medium for sheet metals, metal pipes, and profiles. Fiber laser cutters are used for machinery manufacturing, sheet metal fabrication, electronic circuits, textiles and clothing, leather shoes and bags, car accessories, hardware tools, medical equipment, digital products, instruments, gold and silver jewelry, and craft gifts.
Pros
• Fiber lasers feature with maintenance-free, long service life, high stability, high precision, high speed, high cutting quality, low energy consumption, and environmental protection.
• The fiber laser beam is generated and guided by an integrally flexible medium, allowing for better and easier delivery of the laser beam to the target location.
• Fiber-based lasers offer high output power compared to other different types of lasers.
• Fiber-based lasers offer high optical gain and have active areas exceeding several kilometers.
• Optical fibers have a high surface-to-volume ratio, enabling continuous kilowatt-scale power output with efficient cooling.
• The fiber's waveguide reduces optical path distortion due to thermal issues.
• Fiber-based lasers are relatively more compact than solid-state or gas lasers (with the same power output) and produce a diffraction-limited, high-quality laser beam.
• Fiber-based lasers offer vibration stability, high-temperature tolerance, and extended lifetime at a lower cost.
Cons
• It is usually limited to the field of metal fabrication, and it is unlikely to make a difference in non-metal cutting.
• Fiber lasers are relatively expensive in terms of cost.
• Optical fiber material is easy to break.
• Due to the thin fiber core, the single pulse energy is very small compared to other types of lasers.
YAG Laser Cutter
YAG laser cutting machine is a solid laser cutting system based on yttrium aluminum garnet crystal. The chemical formula of yttrium aluminum garnet is Y3Al5O15, referred to as YAG. Like other solid-state lasers, the basic YAG laser components are working substance, pump source and resonant cavity.
Due to the different types of active ions doped in the crystal, the different pumping sources and pumping methods, the different structures of the resonant cavities used, and the different functional structural devices used, YAG lasers can be divided into many types. According to the output waveform, it can be divided into continuous wave, repeated frequency and pulsed YAG lasers. According to the laser wavelength, it is divided into 1.06μm, frequency doubling, Raman shift and tunable YAG lasers. According to different doping, it can be divided into Nd:YAG lasers and YAG lasers doped with Ho, Tm, Er. According to the shape of the crystal, it can be divided into rod-shaped and slab-shaped YAG lasers. According to different output power, it can be divided into high power, medium power, and low power YAG lasers.
YAG laser cutter expands, reflects and focuses the pulsed laser beam with a wavelength of 1.06 μm, radiates and heats the surface of the material, and the surface heat diffuses to the inside through heat conduction, and the width, energy, peak power, repetition frequency and other parameters instantly melt and vaporize the material, so that the cutting of the predetermined trajectory can be realized through the CNC controller system.
Pros
• YAG laser cutting machine features good beam quality, high efficiency, low cost, stability, safety, precision, and high reliability. It is an ideal precision and efficient flexible cutting tool.
• The cutting speed is fast, the efficiency is high, the economic benefit is good, the straight edge slit is small, the cutting surface is smooth, and the large depth-to-diameter ratio and depth-to-width ratio can be obtained. The thermal deformation is extremely small, and it can be processed on various materials such as hard, brittle, and soft. There is no problem of tool wear and replacement in cutting, no mechanical change, and easy-to-realize automation, and processing can be realized under special conditions. High pump efficiency, up to about 20%. With the increase in efficiency, the heat load of the laser medium decreases, so the beam is greatly improved. Long quality life, high reliability, small size, lightweight, suitable for miniaturized applications.
Cons
• Low photoelectric conversion efficiency and high cost of use;
• There is an internal temperature gradient in the YAG laser rod during the working process, which will cause thermal stress and thermal lens effect, which limits the further improvement of the average power and beam quality of the YAG laser;
• The maintenance of the YAG laser is troublesome, the structure is complicated, and The cost is also relatively high.
• The structure is complex, the power supply is large in size, and requires an optical path to work.
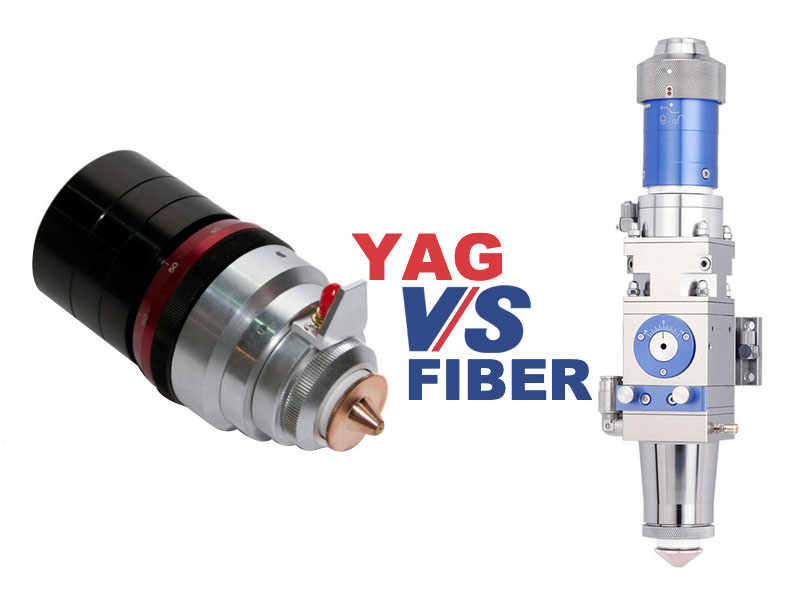
Fiber VS Nd: YAG Laser Cutting Machine
Your choice between the Fiber laser and Nd: YAG laser cutting machine depends on your needs and the materials you are working with, since each of these technologies features certain strengths and weaknesses, making them appropriate for specific uses. Here's a detailed look into their differences that will help understand which is best for the task.
Fiber lasers are modern developments made with efficiency, speed, and low maintenance in mind. This works particularly well in cutting metals such as steel, aluminum, and copper. That is why it has become an industrial favorite when it comes to metal working. With a longer lifespan and lesser operational cost, Fiber lasers serve best in continuous usages and high-production environments.
By contrast, Nd: YAG lasers handle a broader range of materials, extending to some non-metals such as plastics and ceramics. In turn, they are suited for operations that require the highest degrees of detail with high quality, such as implants, instruments, and some aerospace hardware. However, they necessitate periodic servicing because the flash lamps have expendable usage, and the energy output is lower in contrast to fiber lasers.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison to highlight the key differences:
| Feature | Fiber Laser | Nd:YAG Laser |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Medium | Optical Fiber | Crystal (Nd:YAG) |
| Efficiency | High energy efficiency | Moderate efficiency |
| Applications | Metals: steel, aluminum, copper, brass | Metals, plastics, ceramics |
| Precision | High, especially for metal cutting | Excellent for intricate detailing |
| Speed | Faster, especially for thin-to-medium metals | Slower, suitable for precise tasks |
| Lifespan | ~100,000 hours | Shorter lifespan due to flash lamp wear |
| Maintenance | Low, minimal part replacement needed | High, flash lamps require regular replacement |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, lower operational costs | Lower upfront, higher ongoing maintenance |
| Footprint | Compact, modern design | Larger, more traditional setup |
Fiber lasers are ideal for industries focused on high-speed metal processing and cost-efficiency, such as automotive and fabrication shops. In contrast, Nd: YAG lasers are preferred in specialized fields where precision and material versatility are key.
Which is Better for You?
Deciding between a Fiber laser and an Nd: YAG laser cutting machine depends on your specific needs, materials, and priorities. Both machines excel in different areas, so understanding your requirements will help you choose the right option.
Choose a Fiber Laser if:
• You primarily work with metals such as steel, aluminum, copper, or brass.
• Speed and efficiency are crucial for your projects. Fiber lasers cut thinner metals faster and with less energy.
• You want a low-maintenance machine with minimal downtime. Fiber lasers are more reliable with a longer lifespan (~100,000 hours).
• You need a compact machine for a space-efficient setup.
Choose an Nd: YAG Laser if:
• Your projects involve intricate detailing or micro-cutting on metals, ceramics, or plastics.
• Precision is your top priority, especially for industries like medical devices or aerospace.
• You require versatility to process materials other than metals.
• You are willing to invest in regular maintenance and don’t need the machine for heavy, continuous use.
Fiber lasers are better suited for industrial metalworking and high-speed production, while Nd: YAG lasers are ideal for specialized, detailed tasks requiring versatility. Assess your project needs carefully to make the best choice.
How to Choose the Right Laser Cutter for Your Needs
The right selection of the laser cutting machine is cardinal to your projects for reasons of efficiency, precision, and long-term value. Be it a choice between Fiber laser and Nd: YAG laser, a proper understanding of your needs and priorities will guide you toward the best investment. Here's how you can decide:
• Material consideration: Fiber lasers work really great in metals like steel, aluminum, and copper. However, when you are generally working on plastic, ceramic, and all other non-metal materials, you should go for an Nd: YAG laser.
• Consider the Scope and the Speed: As far as running jobs at high speed in continuous production is concerned, nothing outperforms Fiber Lasers. Nd: YAG lasers are the machines to go for if intricate detailing and one-off high precisions are required.
• Evaluate Maintenance vs. Budget: Due to low maintenance and operational costs, fiber lasers tend to be more cost-effective over time. Nd: YAG lasers have a much lower upfront cost but will require periodic maintenance including flash lamp replacement.
• Consider Workspace and Size: Because the fiber lasers are compact, they are much more space-efficient, while Nd: YAG machines are usually bigger in size.