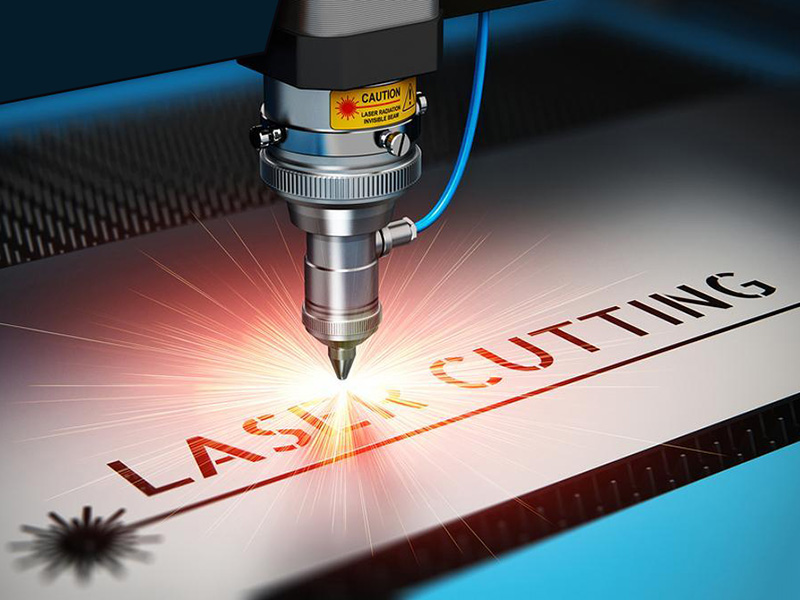
Definition
Laser cutting is a thermal cutting method that uses a focused high-power density laser beam to irradiate the material to be cut, causing the material to quickly heat up and reach the ignition point, and then melt, ablate, vaporize and evaporate to form holes. As the beam moves across the material, the holes grow to form narrower slits, and at the same time, the molten material is blown away by high-pressure working gas to complete a smooth and clean cut.
Principle
The laser uses substance excitation to generate a beam. This beam has a strong temperature. When contacting the material, it can quickly melt on the surface of the material to form a hole. According to the movement of the registration point, the cutting is formed. Compared with the traditional cutting method, the cutting method has a smaller gap and can save most of the material. However, the analysis is defined according to the cutting effect. The material that is cut according to the laser has a satisfactory cutting effect and high accuracy. This is inherited In addition to the advantages of laser, it is also unmatched by ordinary cutting methods.
Types
Laser cutting comes in four categories: vaporization cutting, melting cutting, oxygen cutting, scribing and controlled fracture.
1. Laser vaporization cutting
Using a high-energy density laser beam to heat the workpiece, the temperature rises rapidly, reaches the boiling point of the material in a very short time, and the material begins to vaporize to form steam. The ejection speed of these vapors is very large, and at the same time as the vapors are ejected, a cut is formed in the material. The heat of vaporization of materials is generally very large, so laser vaporization and cutting requires a lot of power and power density.
Vaporization cutting is mostly used for extremely thin metal materials and non-metal materials (such as paper, cloth, wood, plastic and rubber, etc.).
2. Laser melting cutting
In melting cutting, the metal material is melted by laser heating, and then the non-oxidizing gas (Ar, He, N, etc.) is sprayed through the nozzle coaxial with the beam, and the liquid metal is discharged by the strong pressure of the gas to form a cut. Laser melting cutting does not need to completely vaporize the metal, and the energy required is only 1/10 of the vaporization cutting.
Melting cutting is mostly used for materials that are not easily oxidized or active metals, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum and their alloys.
3. Laser oxygen cutting
The principle of laser oxygen cutting is similar to oxyacetylene cutting. It uses a laser beam as a preheating heat source and an active gas such as oxygen as a cutting gas. On the one hand, the blown gas interacts with the cutting metal to cause an oxidation reaction and emit a large amount of heat of oxidation; on the other hand, the molten oxide and melt are blown out from the reaction zone to form a cut in the metal. Because the oxidation reaction in the cutting process generates a lot of heat, the energy required for laser oxygen cutting is only 1/2 of the melting cutting, and the cutting speed is much faster than the vaporizing cutting and melting cutting. Laser oxygen cutting is mostly used for easily oxidized metal materials such as carbon steel, titanium steel and heat-treated steel.
4. Laser scribing and controlled fracture
Laser scribing uses high-energy density laser to scan the surface of the brittle material, so that the material is heated to evaporate a small groove, and then apply a certain pressure, the brittle material will crack along the small groove. Lasers for scribing are generally Q-switched and CO2 lasers.
Fracture control is the use of the steep temperature distribution generated by laser grooving, which generates local thermal stress in the brittle material and breaks the material along the small groove.
Features
Compared with other thermal cutting methods, laser cutting features with fast cutting speed and high quality. Specifically summarized as the following aspects.
1. Good cutting quality
Due to the small cutting spot, high energy density, and fast cutting speed, it can obtain high cutting quality.
a. The cutting incision is narrow, both sides of the slit are parallel and perpendicular to the surface, and the dimensional accuracy of the cut parts can reach ±0.05mm.
b. The cutting surface is smooth and clean, the surface roughness is only tens of microns, without mechanical processing, and the parts can be used directly.
c. After the material is laser cut, the width of the heat affected zone is very small, the performance of the material near the slit is almost not affected, and the workpiece deformation is small, the cutting accuracy is high, the geometry of the slit is good, and the cross-sectional shape of the slit is more Regular rectangle.
2. High cutting efficiency
Due to the features of transmission, the laser cutter is generally equipped with multiple CNC worktables, and the entire cutting process can be fully CNC controlled. During operation, only need to change the numerical control program, it can be applied to the cutting of parts of different shapes, both two-dimensional cutting and three-dimensional cutting.
3. Fast cutting speed
Using a laser with a power of 1200W to cut a 2mm thick low carbon steel plate, the cutting speed can reach 600cm/min; cutting a 5mm thick polypropylene resin board, the cutting speed can reach 1200cm/min. The material does not need to be clamped and fixed during cutting, which can not only save tooling fixtures, but also save auxiliary time for loading and unloading.
4. Non-contact cutting
The cutting torch has no contact with the workpiece, and there is no tool wear. For processing parts of different shapes, there is no need to change the "tool", just change the output parameters of the laser. The cutting process has low noise, small vibration and no pollution.
5. There are many types of cutting materials
Compared with oxyacetylene cutting and plasma cutting, there are many types of laser cuttable materials, including metal, non-metal, metal-based and non-metal-based composite materials, leather, wood and fiber. But for different materials, due to their different thermo-physical properties and different absorption rates for lasers, they show different adaptability for laser cutting.
Applications
Most laser cutters are controlled by CNC programs or made into cutting robots. As a precise processing method, the laser can cut almost all materials, including two-dimensional cutting or three-dimensional cutting of thin metal plates.
In the field of automobile manufacturing, the cutting technology of space curves such as car top windows has been widely used. The German Volkswagen company uses a laser with a power of 500W to cut complex shaped body sheets and various curved parts. In the aerospace field, laser technology is used for cutting special aviation materials, such as titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, nickel alloys, chromium alloys, stainless steel, beryllium oxide, composite materials, plastics, ceramics and quartz. The aerospace parts cut by laser include engine flame tube, titanium alloy thin-walled casing, aircraft frame, titanium alloy skin, wing truss, tail wing panel, helicopter main rotor, space shuttle ceramic heat insulation tile, etc.
Laser cutting technology is also used in the field of non-metallic materials. Not only can cut materials with high hardness and brittleness, such as silicon nitride, ceramics, quartz, etc.; but also can cut and process flexible materials, such as cloth, paper, plastic plates, rubber, etc., such as cutting clothing with laser, can save clothing10 %~12%, improve the efficiency by more than 3 times.
Trends
1. The Laser Cutter Machine will Continue the Epoch-Making Product Revolution.
The laser source is the core component of the cutter, and also an important indicator that determines the type and cutting ability of a laser cutter. Needless to say, future changes in laser cutters will also occur in laser sources. As mentioned above, the replacement of CO2 laser cutting machine by fiber laser cutter is the most important technological revolution in the 40 years since the laser cutter was born, which has brought epoch-making economic benefits to manufacturers and new and old users in this field. So, in the future, will there be a new light source that is cheaper than fiber lasers, has better performance, more excellent beam mode, higher electro-optic conversion rate or lower overall cost? The answer is of course yes. Then ask, what kind of laser? Of course, it is impossible to give an accurate answer now. Science and technology sometimes falter, sometimes thousands of miles a day.
2. High-Power Fiber Laser will Become the Main Force in the Laser Cutting Market.
Nowadays, optical fiber cutting machines of various power ranges have ushered in great development. However, where is the mainstream power of laser cutter machines in the future? Although the machines in each power range have their own use, but the family of lasers that started with high-power fiber lasers and triggered the global laser technology revolution, regard higher power, higher precision, and greater cutting capacity as One of the important development directions of fiber laser cutter. STYLECNC recently launched a 15KW ultra-high-speed fiber laser cutting machine, which has achieved an unprecedented breakthrough in cutting speed and cutting thickness, which has attracted the attention of the industry. Does this contain the future development trend of laser cutters? It is worth looking forward to industry experts, scholars and user friends. In addition, we can be confident that in the near future, many domestic and foreign fiber laser cutter manufacturers will usher in a fierce market competition. Only companies with excellent product quality, continuous focus on R&D investment, and mastering core competitive technologies can do so and be invincible.
3. The Era of Intelligence is Coming.
Whether it is Industry 4.0 in Germany or intelligent manufacturing in China, the fourth industrial revolution in the industrial field is coming. As a high-precision CNC laser cutting machine, the laser cutter will surely keep pace with the times and fly with the technology. The development of laser cutter automation has greatly improved the production capacity and automation level of the sheet metal workshop.
In the future, on this basis, an era of intelligent manufacturing of laser cutters is brewing in the fields of network technology, communication technology, computer software technology and other fields. It is foreseeable that as a means of precision sheet metal blanking, it will inevitably use its own network communication capabilities to communicate with the factory's sheet uncoiling line, bending machine, CNC punching machine, welding (riveting) joint unit, shot blasting and coating line. Other equipment, embedded in a unified production plan, task and assessment management system, has become an important part of the sheet metal workshop management system. As a result, laser manufacturers will gradually transform into sheet metal fabrication contractors.