A laser is a beam of concentrated light energy generated at a specific wavelength. In nature, light exists across a spectrum of wavelengths, ranging from very short (X-rays and gamma rays) to very long (radio waves). Humans can only see visible or the 'white light' wavelengths from around 430-690 nanometers (nm). A laser beam is an amplified concentration of light energy at a specific wavelength. It is coherent light, which allows focusing on a tight spot and a narrow beam over long distances. The word laser is an acronym that stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation.
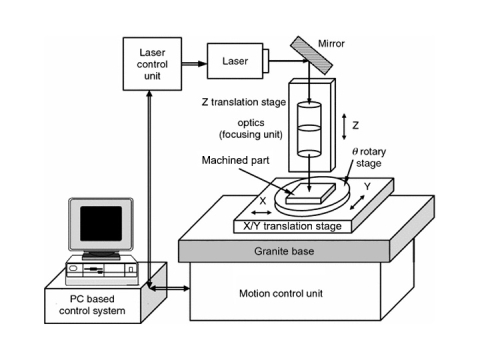
Laser Welder Work Principle
A laser beam is produced inside of the ruby crystal. The ruby crystal is made of aluminium oxide with chromium dispersed throughout it. Which is forming about 1/2000 of crystal, this less than natural ruby. Silver coated mirrors are fitted internally in both sides of the crystal. The one side of mirror has a tiny hole, a beam comes out through this hole.
A flash tube is placed around the ruby crystal, which is filled with xenon inert gas. The flash is specially designed such as which is made flash rate about thousands flashes per seconds.
The electrical energy is converted into light energy, this is worked by flash tube.
The capacitor is provided for storage the electrical energy and supply the high voltage to flash tube for performed appropriately.
The electrical energy discharged from capacitor and xenon transforms the high energy into white flash light rate of 1/1000 per second.
The chromium atoms of ruby crystals are excited and pumped into high energy. Due to heat generating some of this energy is lost. But some light energy reflected mirror to mirror and again chromium atoms are excited until loss of their extra energy simultaneously to form a narrow beam of coherent light. This comes out through the one end tiny hole of crystal’s mirror.
This narrow beam is focused by an optical focusing lens to produce a small intense laser beam on the workpiece.
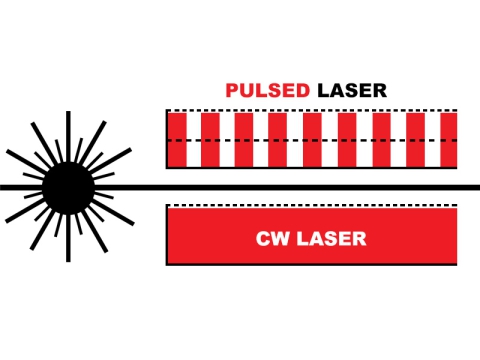
Laser beams change when interacting with material
Laser energy absorption of a material varies based on a number of factors, such as wavelength, material thickness, crystalline structure, material additives, molecular structure, and more. The process takes the advantages of these material properties and laser to create a bond between two plastic materials—one that transmits the laser energy and one that absorbs it.
When a laser beam encounters any material such as plastic, it will either be transmitted, reflected, or absorbed based on the wavelength and the composition of the material it encounters. Most materials exhibit some degree of all three effects, but in varying proportions. A material may be optically clear to light in the visible spectrum and very absorptive to infrared laser, or be opaque to our eyes but transparent to infrared laser.
Laser Welder Mechanics
Laser welding is a process which produces coalescence of materials with the heat obtained from the application of a concentrate coherent light beam impinging upon the surfaces to be joined.
It is achieved through following phases:
1. Interaction of laser beam with workpiece material.
2. Heat conduction and temperature rise.
3. Melting vaporization and joining: When using the laser beam for welding, the electromagnetic radiation impinges on the surface of the base metal with such a concentration of energy that the temperature of the surface is melted vapor and melts of the metal below are formed.